One of the many difficult challenges to increased and sustainable production of fruit and vegetable crops in Africa are fruit flies. They have been identified as a highly economically important group of insects that pose a serious threat to the horticultural industry in sub-Saharan Africa. Fruit fly infestations result in significant losses in yield and quality of fresh fruit, as well as restrictions on exports to sensitive markets throughout Africa. For example, surveys conducted across sub-Saharan Africa have shown that mango crops suffer from infestation by several fruit fly species, including Ceratitis cosyra, C. quinarian and C. capitata especially Bactrocera dorsalis. Mango yield losses can range from 30-70% depending on location, season, and variety (COLEACP-CIRAD, 2009). They feed on a wide range of crops and cause significant damage to a wide range of fruit and vegetable crops.
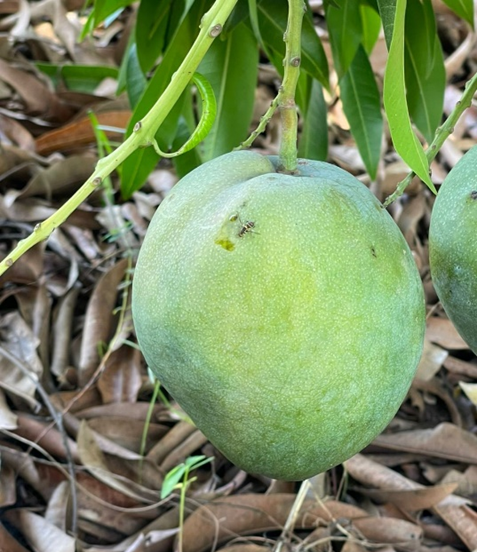

Fruit fly on a Mango, Ivory Coast, May 2023
Andermatt’s Bb-Protec is a biological insecticide that contains spores of the fungus Beauveria bassiana as the active ingredient. When these spores make contact with the target pest insect, the spores germinate and infect the insect, causing what is known as white muscardine disease. A few days later the insect will succumb to the fungus and die.
Typically, Bb-Protec is used against pests such as red spider mite, white fly, false codling moth and mealybug. However, the fruit fly poses unique challenges compared to these pests. Unlike many other pests, the female fruit fly lays its eggs directly inside the fruit, and most of the larval development occurs within the fruit itself. This makes it difficult to target the eggs and larvae directly. Additionally, the adult fruit flies are highly mobile and can evade spray applications. Multiple trials undertaken on mangoes in Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast and Kenya have shown Bb-Protec to be effective in reducing fruit fly damage enhancing marketable yield.
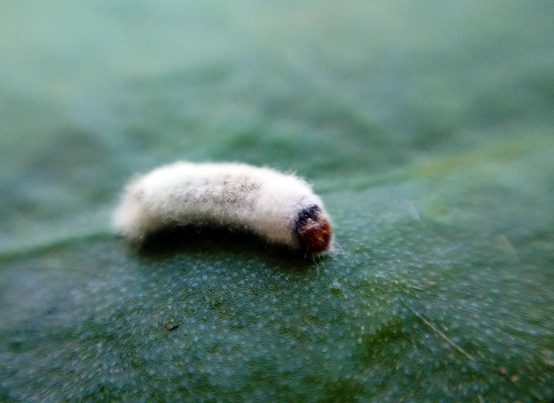

False codling moth infected by Beauveria bassiana R444 (Bb-Protec) showing fungal spores
Table of Bb-Protec registered uses across all markets
| Registered uses* | |
| Pest | Crop |
| Red spider mite | Beans, tomatoes, cucumber, aubergines, ornamentals, berries, stone fruit |
| Whitefly | Beans, tomatoes, cucumber, brinjals, ornamentals, leafy vegetables, brassicas, berries |
| Tomato leafminer | Tomatoes |
| Potato leafminer | Potatoes |
| Mealybug | Pome fruit, citrus, grapes, roses |
| False codling moth | Avocados, litchis, citrus, stone fruit, tree nuts, grapes |
| Woolly whitefly | Citrus |
| Thrips | Beans |
| Fruit fly | Mangoes |
| Coffee berry borer | Coffee |
| Aphids | Beans |
*Registered uses refers to authorised uses in at least one country where Bb-Protec is currently sold
In 2021, three field trials were conducted in separate areas as part of the FIT FOR MARKET SPS program financed by the European Commission and implemented by the Committee Linking Entrepreneurship – Agriculture – Development (COLEAD).
Two trials were conducted in Senegal by the Institut Sénégalais de Recherches Agricoles (ISRA). Bb-Protec was applied 4 times with an application interval of 7 days. A 68% and 64% reduction of attacked fruits was achieved at the dose rate of 600 g/ha of active substance per hectare compared to the untreated control (Figure 1).
The third trial was conducted in Mali by the Institut d’Economie Rurale (IER) using the same spray regime. Bb-Protec reduced the percentage of attacked fruits by 60% compared to the untreated control.
Following these trials, Bb-Protec was registered on mango against fruit fly by the Sahelian Pesticide Committee and in Ivory Coast toward the end of 2022. In total, Bb-Protect is now registered in 10 countries including Burkina, Cabo Verde, Chad, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Senegal, The Gambia and Ivory Coast. Not only will Bb-Protec help growers reduce fruit fly damage, but it has other benefits such as no maximum residue limits which facilitates export, no pre-harvest application interval and certification for organic use.
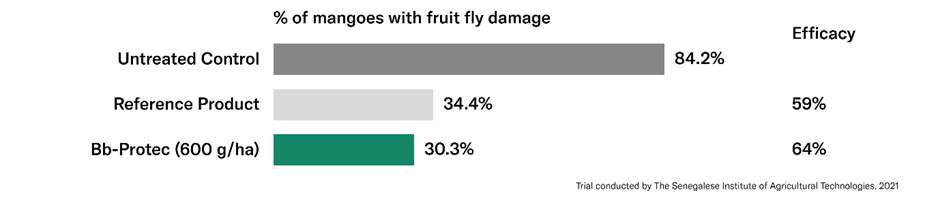
Figure 1: Reduction in the percentage of mangoes with fruit fly damage achieved by Bb-Protec compared to the UTC from the Senegal trial, 2021.
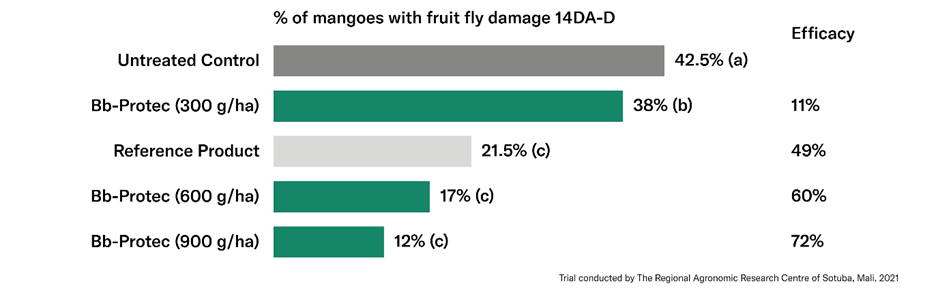
Figure 2: Reduction in the percentage of mangoes with fruit fly damage achieved by Bb-Protec at two different dose rates compared to the UTC from the Mali trial, 2021.
Bb-Protec is an effective biological solution for the control of mango fruit flies. By incorporating this product into pest management strategies, mango farmers will have a tool to successfully mitigate the significant yield losses caused by fruit flies.
References:
World Bank (2008). World Development Report: Agriculture for Development. The World Bank, Washington P. 254
COLEACP-CIRAD (2009). Fighting fruit flies regionally in sub-Saharan Africa. An information letter of the Europe-Africa-Caribbean-Pacific Liaison Committee (COLEACP) and the French Agricultural Research Center for International Development (CIRAD). P.4.

